
At the conclusion of WWII, the United States became embroiled in a Cold War with the Soviet Union. It became evident that in order to evaluate the Soviet strengths and weaknesses, the United States had to have access to aerial surveillance. This culminated in the United States developing “Spy-in-the-Sky” satellites. In June of 1956 Lockheed Aircraft Company was selected to design and build a satellite to be used for continuous surveillance of a potential enemy’s war making capability. Lockheed built the space craft that would house this satellite around Bell Aircraft’s Agena rocket engine.
The Agena rocket engine is a bi-propellant (hypergolic) rocket engine that develops a nominal thrust of 16,000 pounds of force. The engine was used to insert a spy satellite in a desired orbit. The United States developed this satellite under a program called CORONA. In all, there were 145 CORONA launches utilizing the Bell Agena engine. All of these Agena engines were manufactured, assembled and tested at the Bell Rocket Test Facility in Wheatfield, New York.
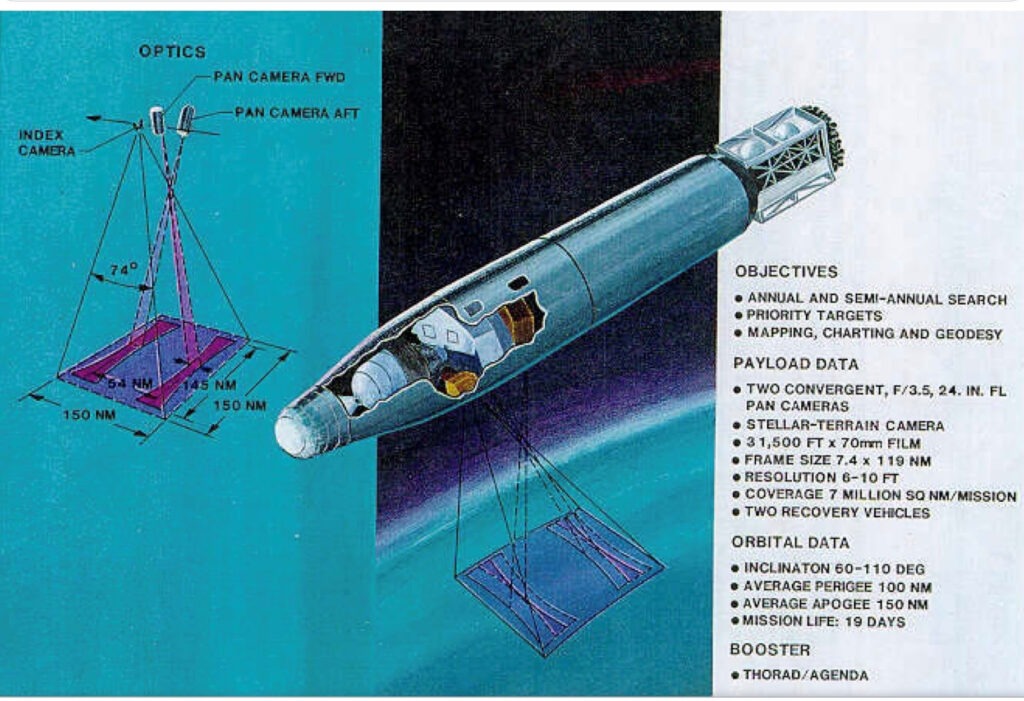
In addition to being used in the CORONA program, the Agena engine was used over 200 times by the United States military and in other major scientific programs such as:
MIDAS – Missile Defense Alarm System. A United States military system of early warning Satellites detecting missile launches, including possible enemy ICBM launches.
SAMOS – The Satellite and Missile Observation System was a series of United States Air Force spacecraft designed to conduct TV surveillance of the entire world by transmitting pictures to earth. Eleven Atlas-Agena and Titan-Agena launches were made between 1960 and 1962.
RANGER – This program was the first of three intermediate steps leading up to the Apollo Program that landed a human on the moon. There were 9 launches, all Atlas-Agena, from 1961 to 1965. Ranger 7 and 8 returned over 11,000 pictures of the moon surface. Ranger 8 landed in the Sea of Tranquility within 15 miles of the intended landing site of the Apollo Spacecraft. Ranger 9 broadcast live on TV 200 pictures of the moon surface.
MARINER – There were 10 Mariner Spacecraft launched between 1962 and 1973. Mariners 1-5 used Agena upper stages. The purpose of these spacecraft was to survey other planets in the solar system. The planets surveyed were Mars, Venus and Mercury.
LUNAR ORBITER – There were 5 Lunar Orbiter Spacecraft launched between 1966 and 1967 by the Atlas-Agena launch vehicles. These spacecraft surveyed 99% of the near side and far side of the moon. Lunar Orbiter 5 returned detailed coverage of five Apollo landing sites.
GEMINI Docking – An Agena vehicle was used as a target vehicle for the Gemini Spacecraft to rendezvous and dock in space. Gemini 8, 10, 11 and 12 proved rendezvous and docking was repeatable and reliable between Gemini spacecraft. It was crucial to demonstrate that this docking maneuver was feasible because during the Apollo program the astronauts in the LEM would have one chance to dock with the Apollo Command Module as they returned from the moon to start their journey back to earth.

Note Agena engine at the near end of the GATV
Contributed by Bruce Blinston
